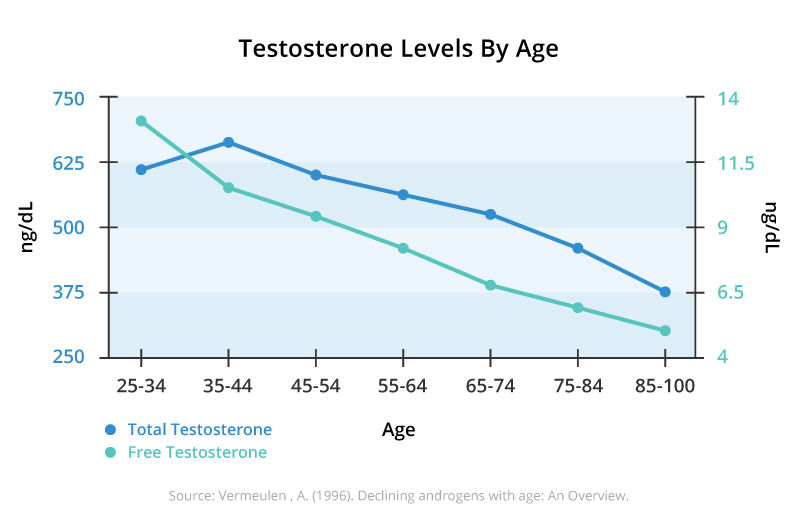
Testosterone, commonly referred to as the “male hormone,” is a crucial factor in the development and maintenance of vital bodily functions in both genders. It is primarily synthesized in men within the Leydig cells of the testes, with a small amount also produced in the adrenal cortex. In men, the typical range for normal testosterone levels is between 300 and 1,000 ng/dl. As men age, there is a gradual decline in testosterone levels, averaging a 1-2% decrease per year beyond the age of 30, resulting in a decline of approximately 100 ng/dl every 10 years. While a natural decline in testosterone levels is expected with aging, abnormally low levels can give rise to various health concerns and significantly impact overall well-being.
Here are 5 signs that you have low testosterone:
1-Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction
A prominent indicator of low testosterone is a noticeable decrease in sex drive. Testosterone is essential for regulating libido in both men and women alike. If you observe a significant decline in your interest in sexual activities, it is advisable to consider undergoing a testosterone evaluation. In men, testosterone plays a critical role in achieving and sustaining erections. Insufficient levels of testosterone can contribute to erectile dysfunction, leading to difficulties in achieving satisfactory sexual performance.
The interplay between androgen levels and sexual performance is intricate. Adequate testosterone levels are essential not only for physical aspects of sexual function, like achieving and maintaining erections, but also for psychological components such as sexual confidence and desire. When testosterone levels are within a healthy range, it can promote a sense of well-being, self-assuredness, and a robust interest in sexual activities.
2-LOW ENERGY AND MOOD CHANGE
Inadequate levels of testosterone can exert a substantial influence on your vitality and overall state of health. If you consistently find yourself grappling with persistent fatigue, even when you’ve had sufficient rest, it might be indicative of an underlying disruption in your hormonal equilibrium. Beyond its more widely recognized roles in sexual health, testosterone also assumes a critical function in governing your emotional well-being and mood stability. Consequently, individuals afflicted with low levels of this hormone may confront a range of emotional challenges, including frequent mood fluctuations, heightened irritability, and even symptoms reminiscent of depression.
The pervasive sense of weariness that often accompanies diminished testosterone levels can pervade your daily life, making even routine activities feel draining and arduous. This unrelenting fatigue can affect your ability to concentrate, engage in physical activities, and maintain an active social life. The continuous battle against exhaustion can erode your enthusiasm for life’s pleasures and limit your capacity to pursue your goals and passions.
3-Decreased Muscle and increased body fat
Testosterone is a fundamental factor in the intricate interplay of our physiological processes, holds a central position in the intricate dance of muscle development and maintenance. When androgen levels fall below the ideal range, a discernible decline in both the size and strength of one’s muscles may become apparent. This reduction in muscular prowess can manifest as weaker physical performance, diminished endurance, and a noticeable decrease in overall physical capabilities.
Beyond its impact on muscle, the ebb and flow of androgen levels can exert a significant influence on our body’s composition. In particular, insufficient androgen levels have been linked to the accumulation of adipose tissue, primarily congregating around the abdominal region. This shift in body composition can contribute to unwelcome weight gain, as the added fat mass not only alters our physical appearance but also presents challenges when it comes to achieving and sustaining weight loss goals.
(Read also: Obesity is killing your manhood.)
4-Reduced Facial and Body Hair
The hormonal changes that occur during puberty play a crucial role in the development of secondary sexual characteristics in males. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, is responsible for various physical changes that take place during this period.
Androgens, a group of hormones including testosterone, promote the growth of facial hair, body hair, and even the deepening of the voice. These changes are commonly associated with the development of masculinity in boys as they transition into adulthood.
During puberty, the levels of testosterone increase, triggering the growth of facial hair, usually starting with a light moustache and gradually progressing to a thicker beard. Body hair, such as chest hair, leg hair, and underarm hair, also begins to appear and becomes more abundant.
In addition to hair growth, testosterone contributes to the deepening of the voice. As the vocal cords lengthen and thicken, the voice becomes lower in pitch and acquires a more mature tone. This change is often one of the most noticeable and characteristic signs of male puberty.
However, it’s important to note that testosterone levels can fluctuate throughout a man’s life. In some cases, individuals may experience a decrease in testosterone levels, which can lead to a reduction in secondary sexual characteristics such as facial hair growth and voice deepening. This can occur due to various factors, including age, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions.
Understanding the role of testosterone and androgens in the development of secondary sexual characteristics can provide insight into the changes experienced by males during puberty. It is a fascinating and complex process that marks a significant transition into adulthood.
5-Neurocognitive symptoms
Research has revealed a correlation between lower testosterone levels and cognitive alterations, encompassing decreased concentration, memory impairments, and challenges in maintaining focus on various tasks. Such findings highlight the potential impact of low testosterone on cognitive functioning.
If you notice any of the 5 signs of low testosterone mentioned above, it’s important to talk to a doctor. They can evaluate your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatments. Lifestyle changes like exercise, a healthy diet, stress reduction, and good sleep can also help improve testosterone levels.
Yours in good health
MDLINE HEALTH


4 thoughts on “FIVE SIGNS OF LOW TESTOSTERONE IN MEN”