Genital herpes (GH) is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus. It is estimated that millions of people worldwide are living with genital herpes, making it crucial to raise awareness and understanding of this condition.
Genital herpes is primarily caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), though HSV type 1 (HSV-1) can also be a factor in some cases. It is typically transmitted through sexual contact with someone who has the virus, either during genital-to-genital contact or oral-to-genital contact. Once infected, the virus remains in the body for life, leading to recurrent outbreaks (read also: Why does your herpes keep coming back?).
Symptoms and signs OF GENITAL HERPES
Many people infected with genital herpes may not experience any noticeable symptoms, which can make the transmission more challenging to prevent. However, when symptoms do occur, they often include:
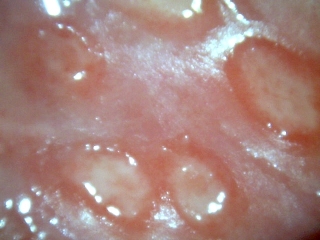
- Small, painful sores or blisters and ulcers in the genital area or rectum.
- Itching, tingling, or burning sensations before the appearance of sores.
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes during the initial outbreak.
It’s important to note that symptoms may vary from person to person, and some individuals may have mild or atypical symptoms.
Transmission and prevention
Genital herpes is primarily spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. The virus can be transmitted even when the infected person does not have any visible symptoms through a process known as asymptomatic viral shedding. To reduce the risk of transmission:
- Practice safe sex by using condoms or dental dams consistently and correctly.
- Be open and honest with sexual partners about your herpes status.
- Avoid sexual activity during active outbreaks or when experiencing symptoms.
Treatment
While there is no cure for GH, antiviral medications (e.g acyclovir) can help manage and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. These medications can also decrease the risk of transmission to sexual partners. Besides medication, individuals can take several self-care measures to cope with genital herpes:
- Maintain good hygiene in the affected area to prevent secondary infections.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction and discomfort during outbreaks.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques, to support the immune system.
Genital herpes is a prevalent sexually transmitted infection that can affect anyone engaging in sexual activity. Open communication with sexual partners, regular STI screenings, and prioritizing emotional well-being are essential steps in managing GH effectively. Remember, knowledge and proactive measures are powerful tools in promoting sexual health and preventing the spread of genital herpes.
Yours in good health
MDLINE HEALTH


One thought on “GENITAL HERPES”